What is Business Model Transformation?
Business model questions and answers are crucial tools for transformation leaders looking to steer their companies into new territories of innovation and growth. As the business landscape becomes increasingly complex and competitive, understanding the nuances of your business model can mean the difference between thriving and merely surviving.
This post delves into key questions that challenge the status quo, encourage strategic thinking, and empower leaders to reimagine the future of their organisations. Whether you're looking to disrupt your industry or ensure your company's long-term viability, these insights will guide you through the process of transformation with clarity and confidence.

Business Model Transformation Course and Certification
What is a Business Model?
A business model is a conceptual framework that outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It encompasses the company's core strategies for operating in its market, including its product or service offerings, target customer segments, revenue streams, value proposition, key activities and processes, resources, partnerships, and cost structure. Essentially, it defines the way a company operates and makes money, detailing the products or services it sells, how it markets and sells those products or services, and how it structures its internal operations and external relationships to support this. A well-defined business model provides a clear roadmap for how the company conducts business, engages with customers, and achieves its financial goals.
What is Business Model Transformation?
Business model transformation refers to the fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of a business's core logic and operations, aimed at achieving significant improvements and competitive advantage in response to shifts in market demands, technological advancements, consumer behaviour, or regulatory changes. It goes beyond mere incremental changes or optimisations of existing processes; it involves changing the way the company creates value for its customers, how it captures that value, and often, the value proposition itself.
This transformation might include diversifying revenue streams, adopting new technologies to deliver services or products more efficiently, redefining customer segments, entering new markets, or changing the way the company engages with customers and partners. The goal is to align the business more closely with current and future opportunities and challenges, ensuring long-term sustainability and growth in a rapidly changing environment.
Business model transformation is driven by the need to adapt to disruptive forces and to capitalise on new opportunities. It requires visionary leadership, a willingness to challenge the status quo, and the capacity to implement profound changes within the organisation. Successful transformations often result in a business that is more agile, innovative, and better positioned to meet the needs of its customers.
What is a Transformative Business Model?
A transformative business model fundamentally changes how a company delivers value to its customers, often leveraging new technologies, innovative processes, or unique market strategies. It involves rethinking the core aspects of the business, including its value proposition, customer base, revenue streams, and operational processes, to better align with changing market demands, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer behaviour. The goal is to achieve significant improvements in performance, reach, and competitiveness.
What Makes a Business Model Transformative?
Several key features distinguish a transformative business model, setting it apart from more traditional or incremental approaches to business. These features enable companies to redefine markets, alter consumer behaviours, and achieve substantial competitive advantages:
Innovation at the Core
At the heart of transformative business models is innovation—whether in products, services, processes, or customer experiences. This innovation often disrupts existing markets or creates entirely new ones.
Customer-Centricity
These models prioritize understanding and meeting the evolving needs and preferences of customers, often delivering personalised experiences or addressing previously unmet demands, thereby enhancing customer value.
Leverage of Technology
Transformative business models frequently utilize cutting-edge technologies to revolutionize product offerings, operational processes, or customer interactions, making technology a key driver of value creation and competitive differentiation.
Agility and Flexibility
They are designed to be agile, allowing businesses to quickly respond to market changes, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer behavior, ensuring long-term relevance and sustainability.
Novel Revenue Streams
Such models often introduce new ways to generate revenue, moving beyond traditional sales or service fees to embrace subscriptions, freemium models, platform ecosystems, or other innovative financial structures.
Value Network Reconfiguration
Transformative models can redefine relationships within and across industries, creating new ecosystems or platforms that connect different market players in mutually beneficial ways, often leading to value network reconfiguration.
Sustainability and Social Impact
Increasingly, transformative business models incorporate sustainability and social impact as integral components, aligning business success with environmental stewardship and social well-being.
Scalability
These models are built with scalability in mind, allowing businesses to expand their reach and impact without proportional increases in costs, often through network effects or digital platforms.
Together, these features enable transformative business models to not just adapt to the changing business landscape but to actively shape it, driving innovation, growth, and change across industries.
Business Model Transformation Versus Digitalisation
Understanding the distinction between “Business Model Transformation” and “Digitalisation” is crucial for any leader navigating the complexities of today's business environment. This knowledge empowers decision-makers to choose the right strategy for their organisation's growth and sustainability.
While digitalisation focuses on enhancing and streamlining operations with technology, Business Model Transformation demands a deeper, more fundamental change to how a company operates and delivers value. Recognising the difference is essential to effectively allocate resources, innovate strategically, and ensure that your company not only keeps pace with the digital revolution but also remains competitive and relevant in an ever-changing market landscape.
Knowing which path to pursue can mean the difference between merely surviving and truly thriving in the digital age.
Business Model Transformation
Business Model Transformation involves fundamentally rethinking how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value. This process requires a significant shift in a company's core operations, strategies, and offerings to adapt to new market demands, technological changes, or competitive pressures. It's about altering the very essence of the business to achieve sustainable growth and a competitive advantage.
What is an Example of Business Model Transformation?
Let's look at three well-known examples of business model transformation.
Netflix Business Model Transformation Example
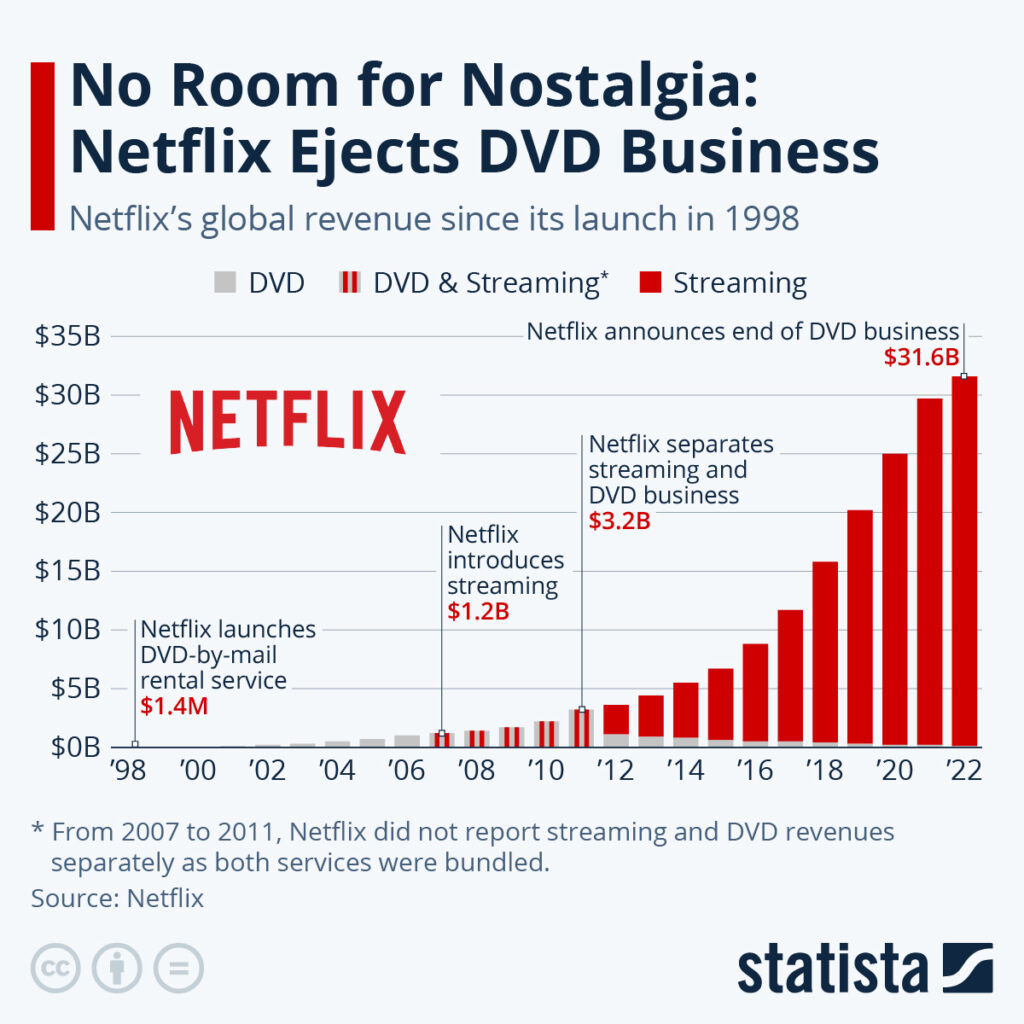
Netflix originally started as a DVD rental service, mailing DVDs directly to customers' homes. Recognising the potential of the internet and changing consumer preferences, Netflix underwent a business model transformation by shifting towards streaming digital content. This move not only diversified their revenue streams through subscription services but also redefined entertainment consumption, making Netflix a global leader in the streaming industry.
Adobe Business Model Transformation Example
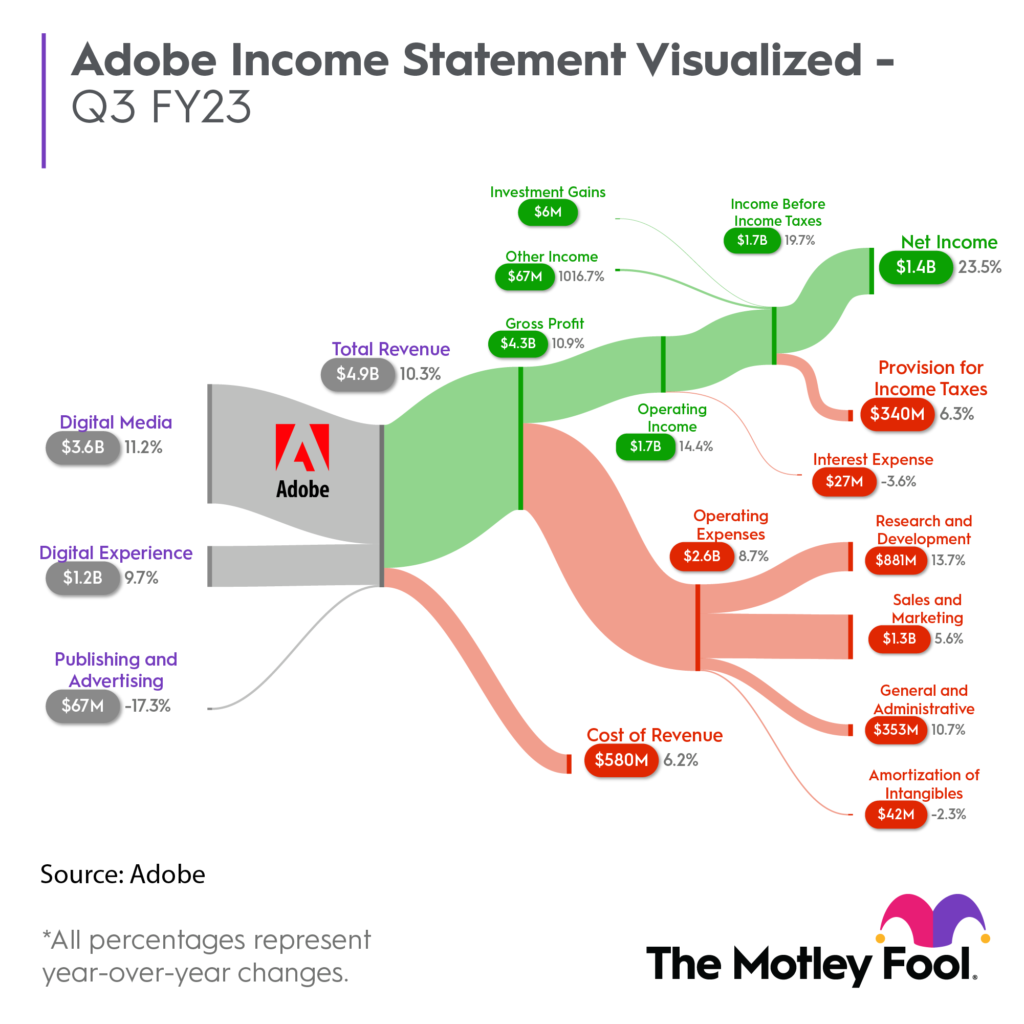
Adobe was once known for selling physical software packages like Photoshop and Illustrator. The company transformed its business model by moving to a cloud-based subscription service, Adobe Creative Cloud. This transition allowed Adobe to offer its suite of software on a subscription basis, providing continuous updates, cloud storage, and a wider range of services. The move significantly increased Adobe's recurring revenue and strengthened its market position in the digital content creation space.
Amazon Business Model Transformation Example
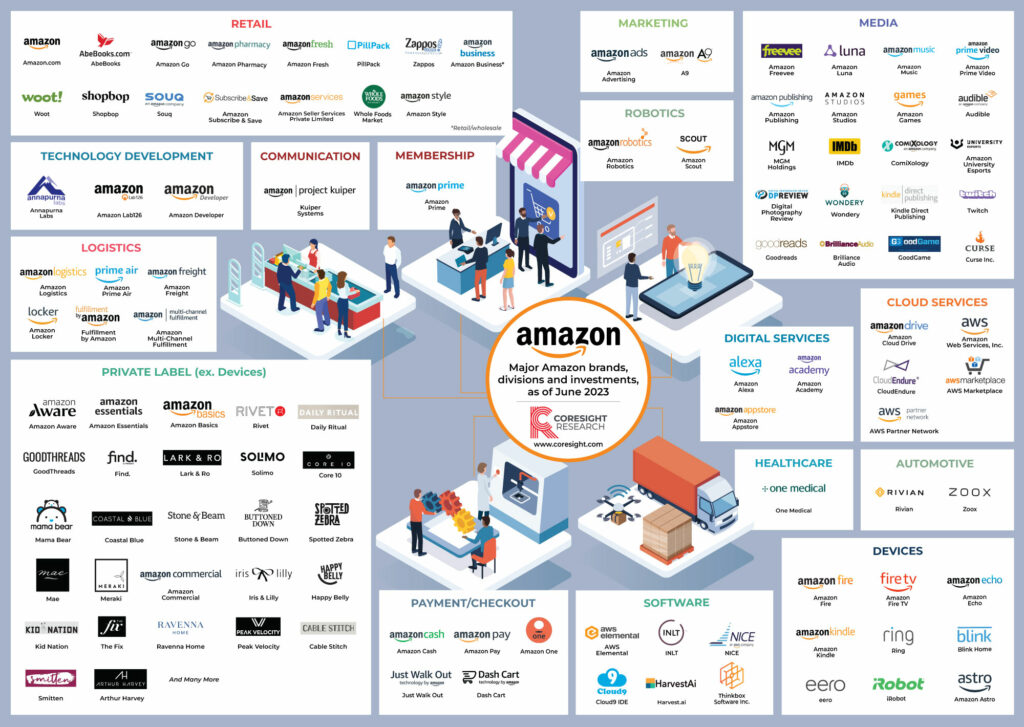
Amazon started as an online bookstore but has since transformed its business model multiple times. It expanded into a vast e-commerce platform that sells virtually everything, from electronics to groceries. Furthermore, Amazon diversified into cloud computing with Amazon Web Services, becoming a dominant player in cloud infrastructure services. This transformation into various sectors has made Amazon one of the most valuable companies in the world, illustrating the power of continuous business model innovation.
50 more business model transformation examples
Digitalisation
Digitalisation, on the other hand, refers to the integration of digital technologies into existing business processes. It's about leveraging digital tools to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, or streamline operations without necessarily changing the core business model or value proposition. Digitalisation aims to optimize and modernise business activities to meet current technological standards.
What is an Example of Digitalisation?
Let's look at three well-known companies that have undergone digitalisation.
Starbucks Digitalisation Example
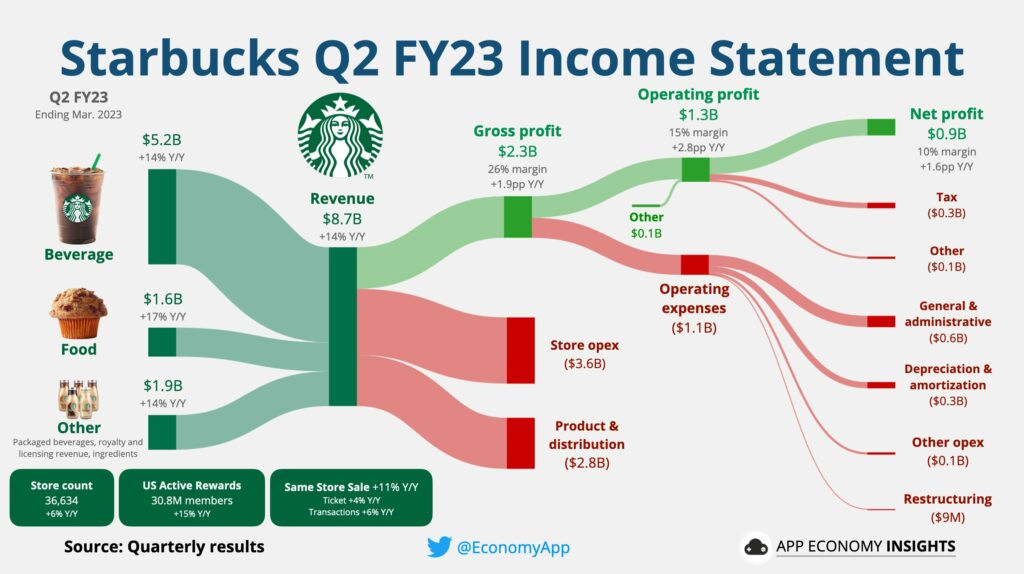
Starbucks embraced digitalisation by launching a mobile app that enables customers to order and pay for their drinks and food in advance. This adoption of digital technology streamlined the customer experience, reducing waiting times and enhancing convenience. The app also provides personalised recommendations and rewards, boosting customer engagement and loyalty.
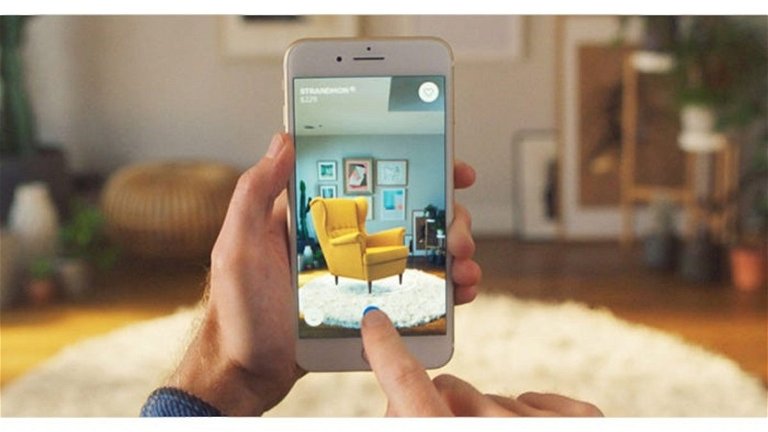
Bank of America Digitalisation Example
Bank of America has significantly digitalised its banking services, offering customers the capability to conduct a wide array of transactions online or through its mobile app. This includes checking account balances, transferring funds, depositing cheques using a smartphone camera, and accessing financial advice. Digital banking has improved accessibility and convenience for customers, diminishing the necessity for physical branch visits.
IKEA Digitalisation Example
IKEA implemented digitalisation through its augmented reality catalogue app, which allows customers to visualise how furniture and decor items would appear in their own homes before making a purchase. By leveraging AR technology, IKEA enhanced the shopping experience, providing customers with a valuable tool to make more informed decisions and reducing the likelihood of returns. This innovative use of digital technology has modernised IKEA’s retail experience, blending physical and digital shopping seamlessly.
What are the 4 Types of Business Models?
In the world of business, understanding the foundational frameworks that companies use to operate and generate revenue is essential. These frameworks, known as business models, define how an organisation creates, delivers, and captures value. They act as the architectural blueprint guiding a company's strategic decisions, operational methodologies, and interactions with customers. By adopting various approaches, from innovative technology use to unique market positioning, these models highlight the strategies businesses employ to establish and maintain their market presence. Delving into the specifics of these models reveals the strategic diversity that enables companies to thrive in their respective industries, offering a closer look at the core principles of successful business management and execution.
Here are four types of business model:
1. Product-Based Business Model
Companies create and sell physical or digital products. This model focuses on manufacturing, product development, and distribution channels.
What is an Example of a Product-Based Business Model?
Let's consider three well-known examples of product-based business models.
Apple Product-Based Business Model
Apple operates under a product-based business model, focusing on the design, manufacture, and marketing of consumer electronics, such as iPhones, iPads, and Mac computers. Apple's success is not just in the innovation and quality of its products but also in its ability to create an ecosystem where customers are encouraged to buy multiple products and services, enhancing user experience and customer loyalty.
Toyota Product-Based Business Model
Toyota is a leading example of a product-based business model in the automotive industry. It designs, manufactures, and sells vehicles globally, including sedans, SUVs, and hybrids. Toyota's business model is underpinned by its reputation for reliability, quality, and innovation in manufacturing techniques like the Toyota Production System, which has set industry standards for efficiency and productivity.
Procter & Gamble Product-Based Business Model
P&G operates a product-based business model focused on a wide range of consumer goods, including personal care, household cleaning, and health products. Brands like Tide, Pampers, and Gillette are developed, manufactured, and marketed to meet various consumer needs. P&G's model emphasises brand management and product innovation to maintain market leadership and customer loyalty.
2. Service-Based Business Model
Businesses offer services instead of tangible goods. This model relies on expertise, customer service, and service delivery mechanisms.
What is an Example of a Service-Based Business Model?
Let's consider three well-known examples of service-based business models.
Accenture Service-Based Business Model
Accenture stands as a beacon in the consulting industry, leveraging its service-based business model to offer a broad spectrum of consultancy services. This includes strategic planning, digital transformation, technological implementation, and operational improvements. By tailoring their expertise to the unique needs of each client, Accenture helps organizations across various sectors achieve their goals and stay competitive in a fast-evolving marketplace.
Spotify Service-Based Business Model
Spotify revolutionised the music industry with its streaming service model, providing users access to millions of songs and podcasts for a monthly subscription fee. Unlike traditional music purchase models, Spotify's service-based approach allows users to explore an extensive library of audio content, create playlists, and discover new music tailored to their tastes, all within an ad-supported free tier or a premium ad-free experience.
Airbnb Service-Based Business Model
Airbnb transformed the hospitality sector with its innovative service-based model, connecting people looking to rent out their homes with travellers seeking accommodations. Instead of owning properties, Airbnb's platform facilitates a marketplace where hosts can list their spaces and guests can find unique places to stay around the world. This model has not only expanded lodging options for travellers but also created new income opportunities for individuals, showcasing the power of community-driven service models in the digital age.
3. Subscription-Based Business Model
Customers pay a recurring fee to access a product or service. This model emphasises customer retention and value over time.
What is an Example of a Subscription-Based Business Model?
Let's consider three well-known examples of subscription-based business models.
Headspace Subscription-Based Business Model
Headspace takes a unique approach to mental well-being through its subscription-based model, offering guided meditations, mindfulness practices, and sleep aids. Catering to individuals looking to improve their mental health and overall wellness, Headspace provides access to a vast library of content designed to support various aspects of well-being, from stress reduction to focus enhancement, making it a leader in the digital health space.
Birchbox Subscription-Based Business Model
Birchbox pioneered the subscription box model in the beauty industry, offering monthly boxes of personalized beauty samples to its subscribers. This approach not only provides customers with a convenient way to discover new products tailored to their preferences but also creates a unique unboxing experience that has contributed to the company's success.
Peloton Subscription-Based Business Model
Peloton combines its high-end fitness equipment with a subscription-based content model, offering live and on-demand fitness classes to its users. Subscribers can access a wide range of workouts, from cycling and running to strength training and yoga, directly from their Peloton equipment or app, creating a comprehensive at-home fitness solution. This model has distinguished Peloton in the fitness industry by integrating premium hardware with immersive content.
4. Platform-Based Business Model
Companies create a platform that facilitates interactions or transactions between different user groups, often taking a fee for each transaction. This model leverages network effects to grow.
What is an Example of a Platform-Based Business Model?
Let's consider three well-known examples of platform-based business models.
Twitch Platform-Based Business Model
Twitch has carved a niche for itself in the live streaming industry with a platform-based business model that primarily caters to the gaming community. It connects streamers with viewers, allowing gamers to broadcast their gameplay while interacting with their audience in real-time. Twitch monetises through advertising, subscriptions to streamer channels, and the sale of virtual goods that enhance the viewing experience.
Rover Platform-Based Business Model
Rover is an online marketplace for pet services that embodies a platform-based business model. It connects pet owners with service providers who offer dog walking, pet sitting, boarding, and grooming services. Rover's platform facilitates these connections, ensuring safety and reliability with features like secure messaging and payments, while generating revenue by taking a percentage of each booking.
Skool Platform-Based Business Model
Skool leverages a platform-based business model to revolutionise online education by facilitating the creation and management of online communities and courses for educators. This platform distinguishes itself through its emphasis on interaction and community engagement, offering features that support discussion, collaboration, and progress tracking. Educators can monetise their content through subscriptions or course fees, while learners gain a more structured and communal online learning experience. Skool's user-friendly approach aims to enhance the digital education landscape by fostering a vibrant learning community.
What is an Example of a Business Model Transformation Process?
An example of a business model transformation process is the journey undertaken by Adobe Systems. Adobe, originally known for selling boxed software products like Photoshop and Illustrator, transformed its business model to a subscription-based service known as Adobe Creative Cloud.
1. Recognition
Adobe recognised the shift in consumer preference towards digital services and the need for constant updates and innovation in software tools. The rise of internet piracy also highlighted the limitations of the traditional one-time purchase model.
2. Conceptualisation
Adobe envisioned a new model that would provide users with the latest software updates, cloud storage, and collaborative tools for a monthly or annual subscription fee. This would not only address piracy concerns but also offer a steady revenue stream and improve customer satisfaction through continuous innovation.
3. Implementation
In 2013, Adobe initiated the transition by discontinuing the sale of physical software boxes and moving entirely to the Creative Cloud subscription model. This involved significant changes in its software development, distribution, sales strategy, and customer support.
4. Optimisation
Over the years, Adobe has continually optimized its subscription model by adding new features, applications, and cloud-based services to enhance value for its subscribers. The company has also expanded its target market beyond professional designers and content creators to include hobbyists and educators, further broadening its revenue base.
This business model transformation has been highly successful for Adobe, resulting in a substantial increase in recurring revenue, a higher market valuation, and a more engaged and loyal user base. Adobe's shift to a subscription-based model is often cited as a textbook example of how established companies can successfully navigate digital transformation, demonstrating the potential of adapting business models to changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
What are the 4 Stages of Business Model Transformation?
Diving into Business Model Transformation reveals a structured journey through four distinct stages. This progression is crucial for organisations seeking to fundamentally redefine how they create, deliver, and capture value in response to shifting market landscapes and emerging opportunities. Up next, we explore these critical phases, offering a concise overview of each step in the transformative journey of a business model. This segment serves as a guide for leaders and visionaries intent on steering their organizations toward innovative horizons, ensuring a methodical path to profound and impactful change.
The four stages of Business Model Transformation encapsulate the journey an organization undertakes to fundamentally redefine its core operations and strategy. These stages are:
1. Business Model Initiation
This stage involves recognising the need for change. It's driven by external pressures like technological advancements, competitive threats, or shifts in consumer behaviour. During initiation, companies assess their current model's sustainability and explore the potential for transformation.
2. Business Model Conceptualisation
Here, organizations develop a clear vision of the future state of their business model. This involves identifying new value propositions, innovative revenue streams, and different ways of operating. Strategic planning, market research, and feasibility studies are critical in this phase to outline the transformation blueprint.
3. Business Model Implementation
The focus shifts to putting the planned changes into action. This could involve developing new products or services, adopting new technologies, restructuring operations, or entering new markets. Effective change management, stakeholder engagement, and agile project management are key to navigating this stage successfully.
4. Business Model Consolidation and Scaling
In the final stage, the transformed business model is refined, optimised, and prepared for scaling. Organisations monitor performance, gather feedback, and make necessary adjustments to ensure the new model is sustainable and scalable. The goal is to fully integrate the changes into the organisational fabric and leverage them for competitive advantage and growth.
Navigating these four stages effectively requires visionary leadership, a willingness to embrace change, and a strategic approach to managing the transformation process.
How Many CEOs Prioritise Business Model Transformation?
An increasing number of CEOs are recognising the importance of building new businesses – which of course requires innovative business models. These are the CEOs who know they need to go beyond basic digitalisation, if they want to follow in the footsteps of CEOs like Reed Hastings of Netflix.
While everyone around a CEO has an opinion, most don’t have the skills required to guide and advise their CEO when it comes to building new businesses with new business models.
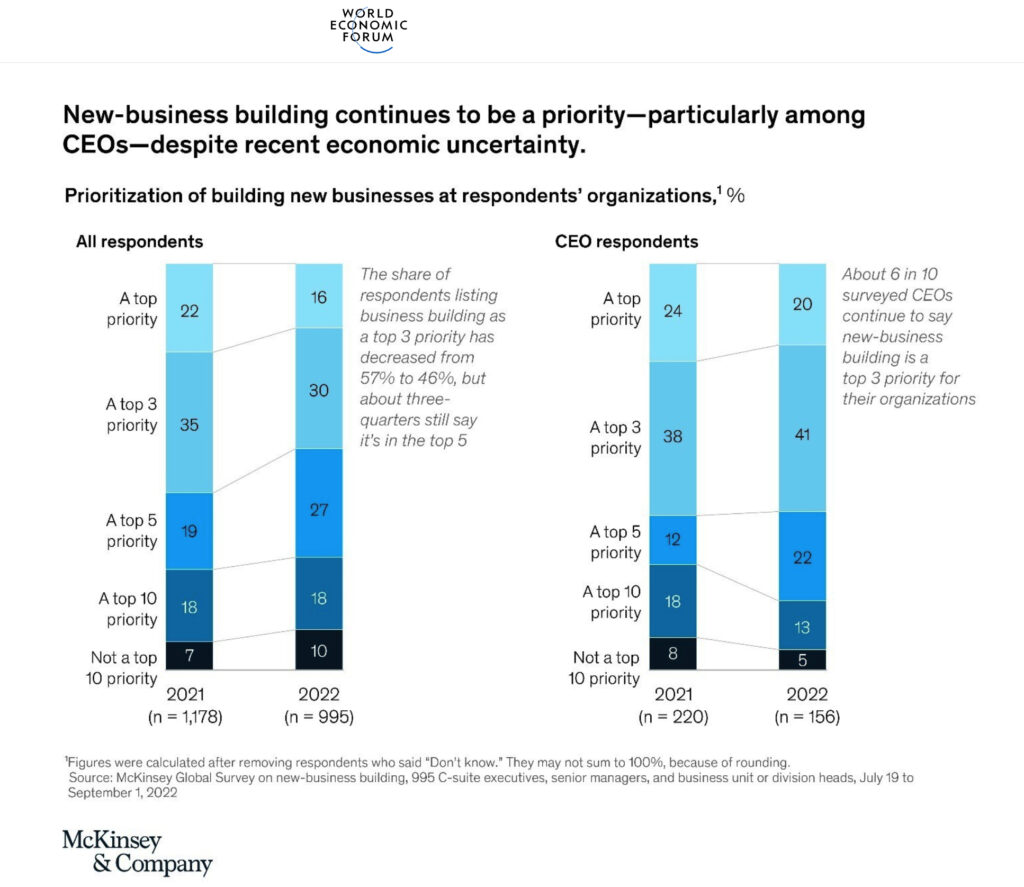
The data from a McKinsey survey suggests that 61% of CEOs placed starting new ventures among their top three priorities. When most CEOs have only inherited existing businesses, and have never built a new business, that leaves a lot of CEOs needing help.
What Business Model Transformation Course?
Most transformation courses are focused on digitalisation, which addresses what most companies are pre-occupied with. The latest Business Model Transformation course is available online at the CXO Transform platform, and the structure is outlined below.
