Digital Art – The Masterpiece
Digital art is a form of art that utilises digital technology for its creation and presentation. It is a rapidly growing field that is changing the way we view and interact with art.
Digital art has expanded the boundaries of what is possible, allowing artists to create interactive installations, immersive experiences, and augmented reality works. It is often characterised by its use of new media technologies, such as virtual and augmented reality, digital projection, and motion graphics. Its versatility and accessibility have made it a popular medium for both established and emerging artists.
As the technology continues to evolve, digital art will undoubtedly continue to push the boundaries of traditional art forms and expand our understanding of the creative process.

What is Digital Art?
Digital art is a rapidly growing field that is changing the way we view and interact with art. It has expanded the boundaries of what is possible, allowing artists to create interactive installations, immersive experiences, and augmented reality works. Digital art is often characterised by its use of new media technologies, such as virtual and augmented reality, digital projection, and motion graphics. Its versatility and accessibility have made it a popular medium for both established and emerging artists. As the technology continues to evolve, digital art will undoubtedly continue to push the boundaries of traditional art forms and expand our understanding of the creative process.
What Are The Benefits of Digital Art?
There are many benefits of digital art, including:
Versatility
Digital art provides a range of creative possibilities that traditional media cannot achieve. It allows artists to experiment with different styles and techniques, from realistic illustrations to abstract compositions.
Accessibility
Digital art is more accessible than traditional art forms, as it does not require specialised equipment or materials. With just a computer and digital art software, artists can create professional-grade art.
Time-saving
Digital art is a time-saving medium. Unlike traditional art forms, it is faster and easier to make edits and revisions to digital artwork.
Cost-effective
Digital art is a cost-effective medium, as it does not require the purchase of expensive art supplies or equipment.
Environmentally friendly
Digital art is more environmentally friendly than traditional art forms, as it reduces the amount of waste created from discarded art supplies.
Collaboration
Digital art allows artists to collaborate with others around the world in real-time. This can lead to new creative opportunities and collaborations that would not be possible with traditional art forms.
Preservation
Digital art is more durable than traditional art forms, as it can be easily stored and reproduced without damaging the original artwork.
Digital art provides a wide range of benefits that make it an attractive medium for artists and art enthusiasts alike.
The History of Digital Art
The history of digital art can be traced back to the 1950s when computer technology was first used to create art. One of the first examples of digital art was a computer-generated pattern created by a computer scientist named Ben Laposky in 1950. However, it wasn't until the 1960s that artists began to use computers to create digital art.
During the 1960s and 1970s, computer technology became more advanced, and artists began to use it to create a wide range of artworks. This led to the emergence of new forms of art, such as computer-generated images, animations, and interactive installations.
In the 1980s, digital art became more accessible to a wider audience as personal computers became more affordable. The development of computer graphics software also made it easier for artists to create digital art.
In the early 1980s, the term “digital art” was first used to describe artworks made with the use of a paint program developed by computer engineers. This innovative technology was used by Harold Cohen, a pioneering digital artist who created AARON – a robotic machine designed to draw large images on paper placed on the floor. Since then, Cohen has continued to refine the AARON program in step with advancing technology.
Since then, digital art has continued to evolve and has become a prominent form of contemporary art. Today, digital art can be created using a wide range of technologies, including computer software, virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence.
Following some initial reluctance, digital technology has drastically altered various artistic practices including painting, literature, drawing, sculpture, and music/sound art. In addition, new techniques, such as internet art, digital installation art, and virtual reality have emerged as a result of this transformation.
Digital Art Fun Fact
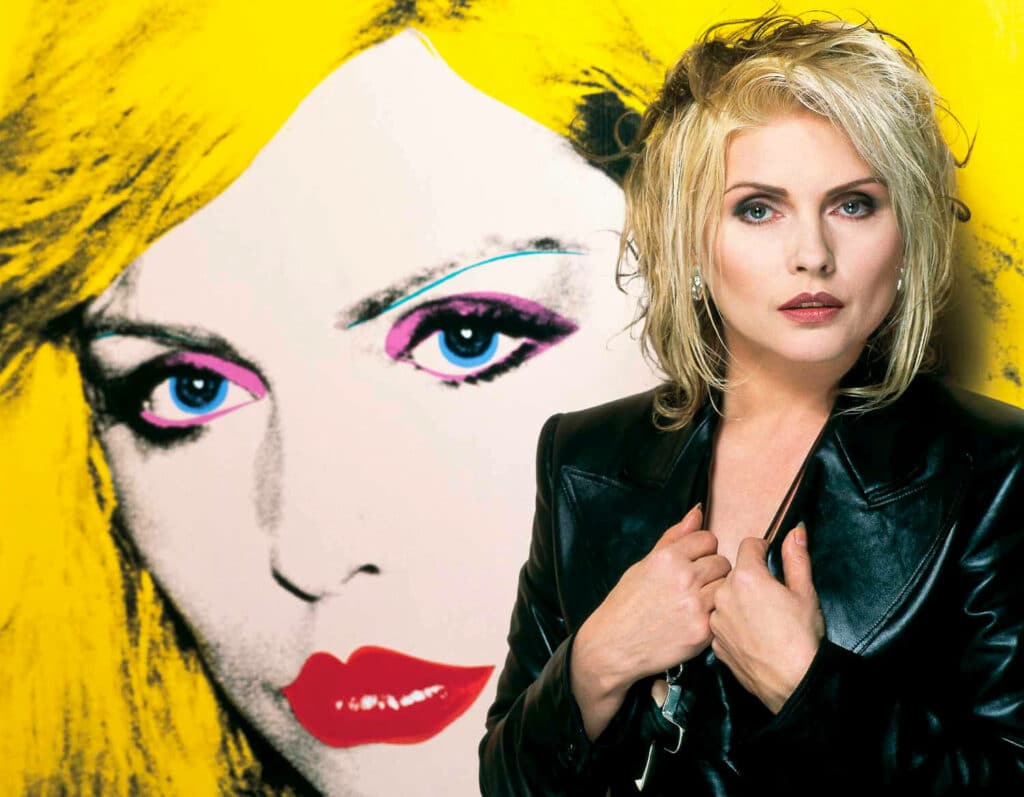
Using a Commodore Amiga, Andy Warhol introduced digital art publicly at the Lincoln Center in New York in July 1985. He captured a monochrome image of Debbie Harry from a video camera and digitised it into a graphics program called ProPaint. Warhol added colour to the image using flood fills to manipulate it.

Digital Art and Business
Digital art can play a significant role in business, particularly in industries such as advertising, marketing, and entertainment. In advertising and marketing, digital art can be used to create eye-catching and visually appealing campaigns that capture the attention of the target audience. Digital art can also be used in the entertainment industry to create immersive experiences and special effects in movies, video games, and other media.
Moreover, digital art can also be used in the business world to create infographics, data visualisations, and other forms of visual communication that can make complex information more accessible and easier to understand. Additionally, businesses can use digital art to create corporate branding, logos, and other visual elements that help to establish their brand identity and differentiate them from their competitors.
In summary, digital art has a wide range of applications in the business world, and companies that incorporate digital art into their operations can gain a competitive advantage by creating visually compelling campaigns, communicating complex information more effectively, and establishing a strong brand identity.
What is NFT Art?
NFT art, or non-fungible token art, refers to digital artwork that is certified on a blockchain network. NFTs are unique digital assets that allow artists and collectors to authenticate and track ownership of digital artwork.
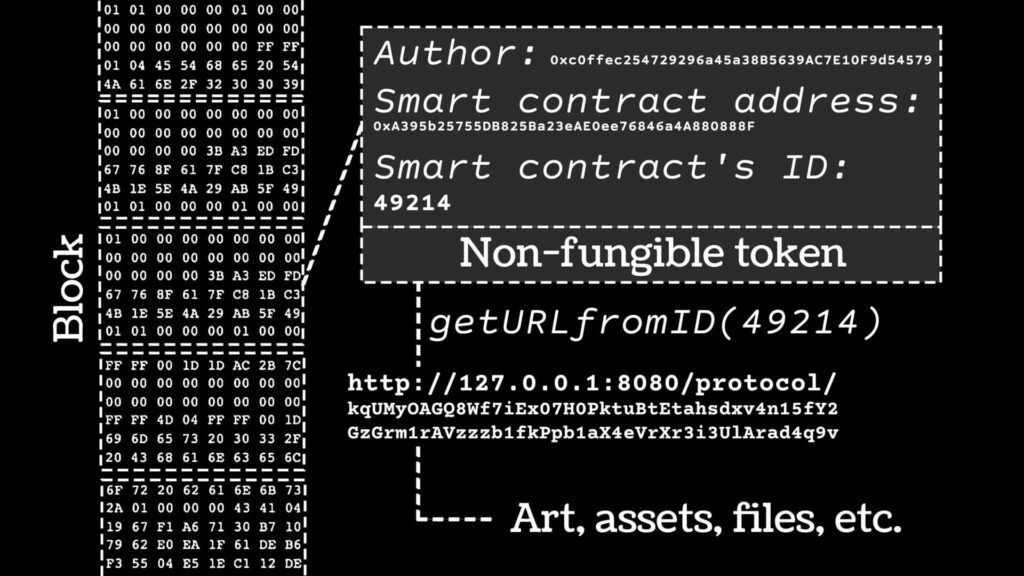
Each NFT is created on a blockchain and contains a unique code that proves ownership of a specific digital asset, such as an image, video, or audio file. NFT art has gained popularity in recent years as a new way for artists to sell their digital works and for collectors to invest in unique pieces of art. NFTs have also been used to sell other digital assets, such as virtual real estate and game items.
Why is NFT Art Worth Anything?
The value of NFT art is based on the same principles as traditional art: scarcity and perceived value. NFT art is unique and limited, which increases its scarcity, and it's worth as much as someone is willing to pay for it. The blockchain technology used for NFTs allows for proof of ownership, which adds to the perceived value of the artwork. Additionally, some buyers see NFT art as a new asset class with potential for appreciation, which can drive up its value. Overall, the value of NFT art is ultimately determined by the market and the demand for it.
Why do People Buy NFT Art?
People buy NFT art for various reasons, including:
Status and Ownership
Owning an NFT art piece provides a sense of ownership and status as a collector of unique, one-of-a-kind digital art that is verified on the blockchain.
Investment
Some people see NFT art as an investment opportunity, with the potential for a high return on investment in the future.
Support for Artists
Purchasing NFT art can be a way to support artists by providing them with a new source of revenue that bypasses traditional gatekeepers, like galleries or art dealers.
Access
Collectors may be drawn to NFT art because it offers a new way to access art that they may not have had access to otherwise, such as exclusive drops or collaborations between artists and brands.
Innovation and Technology
NFT art represents a new frontier in art that is at the intersection of innovation and technology, which may appeal to some collectors who are interested in the cutting edge of digital art.
NFT Digital Art and the Metaverse
NFT digital art has gained increased attention in recent years, particularly in the context of the metaverse. The metaverse is a virtual universe where users can interact with each other in a digital world, using avatars to represent themselves.
As the metaverse becomes more popular, the demand for unique and collectible digital assets, including NFT digital art, has grown. NFTs allow for the creation of unique digital assets that can be bought and sold, even in virtual worlds. This has opened up a new market for digital artists and collectors alike.
In the metaverse, NFT digital art can be displayed in virtual galleries, museums, and even private collections, just like in the physical world. These virtual spaces offer a new way to experience and interact with art, enabling people from all over the world to view and appreciate it.
Furthermore, the metaverse offers a unique opportunity for digital artists to create immersive experiences with their NFT digital art. For example, an artist could create a virtual world where visitors can explore and interact with their artwork in ways that are not possible in the physical world.
Overall, the metaverse is an exciting new frontier for NFT digital art, offering new possibilities for creation, curation, and appreciation of digital art. As the metaverse continues to evolve, it is likely that NFT digital art will become even more important and valuable in this digital landscape.
The World's Most Expensive NFT Art
“Everydays: the First 5000 Days” is a digital work of art created by Mike Winkelmann known professionally as Beeple. The work is a collage of 5000 digital images created by Winkelmann for his Everydays series. Its associated non-fungible token (NFT) was sold for $69.3 million at Christie's in 2021, making it the most expensive non-fungible token ever.
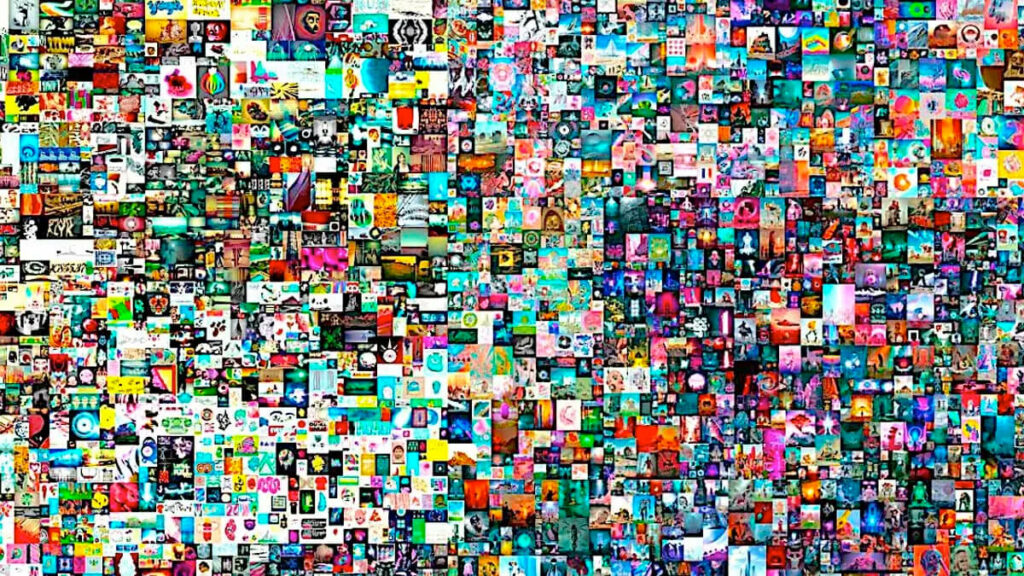

The buyer of the art, Vignesh Sundaresan, is a cryptocurrency investor and the founder of the Metapurse NFT project, based in Singapore. While he has the right to display the artwork, he does not have the copyright. He has showcased the artwork in a digital museum located within “the metaverse”, which can be accessed by the public through a web browser.
Digital Art and Traditional Artists
Digital art and traditional artists are not mutually exclusive, and many artists today use a combination of both. Digital tools have opened up new possibilities for traditional artists, allowing them to experiment with new techniques and create new works of art. At the same time, digital artists often draw inspiration from traditional art forms and techniques, blending them with modern digital tools to create unique pieces. There is no single “right” way to create art, and both digital and traditional techniques can be used to create beautiful and meaningful works.
Digital Art and Sustainability
Digital art is often seen as a more sustainable alternative to traditional art forms, as it has a much lower environmental impact. The creation and exhibition of traditional art often requires the use of materials that are not eco-friendly, such as oil paints and chemicals, as well as the transportation of heavy and bulky works of art.
On the other hand, digital art is created and exhibited through digital technologies, which have a much smaller environmental impact. The production of digital art does not require the use of physical materials, such as canvas, paints, and brushes, and it can be shared and displayed through digital platforms, which reduces the need for transportation.
In addition, the emergence of blockchain technology has created new opportunities for digital art to be used in innovative ways to promote sustainability. Blockchain can be used to create digital art that is linked to sustainable practices or to track the provenance of eco-friendly materials used in art production.
Overall, digital art can contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing the environmental impact of the art industry and by leveraging innovative technologies to promote sustainable practices.
Blockchain and Digital Art
Blockchain technology is being used in the art world to provide proof of authenticity, ownership, and provenance for digital art. This is important because digital art is often copied, modified, and distributed without the knowledge or consent of the artist, making it difficult to prove who owns the original artwork or who has the right to sell it.
By using blockchain technology, digital art can be stored and tracked on a decentralised, tamper-proof ledger that allows artists to retain control over their work and prove its authenticity. This can help to establish a more transparent and fair market for digital art, as buyers can be confident that they are purchasing a legitimate piece of art and artists can be fairly compensated for their work.
In addition to providing a secure and transparent platform for buying and selling digital art, blockchain technology can also be used to create new revenue streams for artists. For example, some platforms are using blockchain to allow artists to sell limited editions or even one-of-a-kind digital works, which can be purchased and collected like traditional physical artwork.
Overall, the use of blockchain technology in digital art has the potential to revolutionise the way we view, buy, and sell art in the digital age, while also helping to address some of the sustainability challenges facing the art world.
Artificial Intelligence Art
Artificial intelligence (AI) art refers to artworks created using artificial intelligence techniques, such as deep learning, computer vision, and natural language processing. These techniques allow AI systems to generate and manipulate images, videos, music, and other forms of media, often in unexpected and creative ways. AI art can be created by human artists using AI tools, or by AI systems operating autonomously, with or without human input. The use of AI in art has sparked new debates and discussions about the role of creativity, authorship, and aesthetics in the age of intelligent machines.
One of the most common forms of AI art is generative art, which involves using algorithms and machine learning techniques to create unique works of art. Generative art can be created using a variety of tools, such as neural networks, genetic algorithms, and more.
AI art is also being used in other fields, such as advertising and fashion. For example, fashion designers are using AI algorithms to create new clothing designs and patterns, while advertisers are using AI-generated images and videos to promote products and services.
While AI art is still a relatively new field, it is rapidly growing and evolving, and is expected to play an increasingly important role in the world of art and design in the coming years.
Well Known Digital Artists
There are many well-known digital artists who have gained popularity in recent years. Here are a few examples:
Joshua Davis – a designer and artist known for his experimental digital works and interactive installations.
Rafael Lozano-Hemmer – a Mexican-Canadian artist who creates large-scale, interactive installations that often incorporate digital technology.
Golan Levin – an American artist, designer and engineer who explores the intersection of art and technology, creating interactive installations and performances.
Manfred Mohr – a pioneer in the field of digital art, who has been creating algorithmic art since the 1960s.
Cory Arcangel – an American artist who works with a variety of media, including video, performance, and digital art. He is known for his use of found digital materials, such as obsolete computer hardware and software, to create new works of art.
These are just a few examples, but there are many more talented digital artists working in a variety of styles and mediums.
Digital Art Use Cases
Digital Art for Advertising and Marketing
Digital art has also found applications in advertising and marketing. The use of digital art in advertising campaigns has become increasingly popular due to its versatility, ability to create unique visuals, and low cost compared to traditional methods. It allows for the creation of dynamic, attention-grabbing content that can be easily distributed across various digital platforms.
Digital art can be used for creating custom graphics and illustrations for marketing materials such as brochures, websites, social media, and other promotional materials. It can also be used to create engaging and interactive content such as animations, infographics, and videos.
One popular trend in digital art for advertising is the use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to create immersive and interactive experiences for consumers. Brands are leveraging AR and VR to create product demos, immersive brand experiences, and interactive ads that allow users to engage with their products in a virtual environment.
Digital Art for Film and Animation
Digital art has also revolutionised the fields of film and animation, allowing for incredible special effects, computer-generated imagery (CGI), and animated films. Digital art software and tools are used extensively in the creation of films, TV shows, and animated features, allowing filmmakers to bring their visions to life and tell stories in entirely new ways.
For example, Pixar Animation Studios is known for using digital art tools and techniques to create their critically acclaimed films, such as Toy Story, The Incredibles, and Finding Nemo.
Digital art has also allowed for more efficient and cost-effective filmmaking, with the ability to create realistic environments, characters, and effects without the need for physical sets or practical effects.
Digital Art for Gaming
Digital art is a crucial component of modern gaming, with game developers relying on digital art to create immersive and engaging gaming experiences for players. From concept art and character design to environmental art and animations, digital art is used to bring video game worlds to life.
Game development teams use digital art to create a range of assets, including 2D and 3D graphics, textures, animations, and visual effects. Digital artists work closely with game designers and developers to ensure that their artwork aligns with the game's concept and narrative, and they also ensure that the artwork meets technical requirements such as file size and format.
Digital art in gaming has come a long way since the days of 8-bit graphics and pixel art. With advancements in technology, modern video games feature stunning visuals, complex animations, and lifelike environments that provide players with a sense of immersion and realism. Digital art also plays a key role in the development of virtual reality (VR) games, which aim to provide players with a completely immersive experience by creating realistic and interactive virtual worlds.
Digital Art for Education
Digital art has also found various applications in education, particularly in teaching art and design. It allows for new forms of creativity and enables students to create and manipulate artwork in ways that were not possible before. Digital art software and tools allow for easy experimentation, layering, and undoing, making the process of creating art more accessible and less intimidating for learners.
Moreover, digital art can also be used to create interactive educational materials such as e-books, animations, and other visual aids. These materials can engage learners in a more immersive and interactive way, making the learning experience more engaging and effective. Digital art can also be used to create digital portfolios and online galleries, providing students with an opportunity to showcase their work and receive feedback from a broader audience.
Digital Art for Virtual and Augmented Reality
Digital art is increasingly being used in virtual and augmented reality applications. With the development of VR and AR technology, artists can create immersive and interactive experiences for users that combine digital art with the physical world.
For example, digital art can be used to create virtual environments for educational purposes, such as historical reenactments, or for entertainment, such as in video games and virtual theme parks. Augmented reality can also be used to overlay digital art onto the physical world, such as in public art installations or in advertising campaigns.
The possibilities of digital art in VR and AR are endless, and the field is constantly evolving as technology continues to advance.
Digital Art for Interior Design and Architecture
Digital art can also be used in interior design and architecture to create realistic visualisations of interior spaces and buildings. By using software such as 3D modelling and rendering programs, designers and architects can create virtual environments to showcase their designs and concepts to clients. These digital art renderings can also be used to explore different design options and make changes before beginning the actual construction process, which can save time and money.
Digital art can also be used to create interactive installations and visual displays in interior spaces, such as museums and exhibitions, that enhance the visitor experience.
Digital Art for Fashion and Textiles
Digital art has made a significant impact on the fashion and textiles industry, particularly in areas such as textile design, pattern making, and fashion illustration. With digital tools, designers and artists can experiment with colors, patterns, and textures, and create intricate designs that would be difficult to achieve with traditional techniques.
Digital printing technologies have also revolutionised the way fabrics and textiles are produced, allowing for greater efficiency and flexibility in the manufacturing process. In addition, digital art is increasingly being used to create unique and customised fashion pieces, such as digitally printed dresses, scarves, and accessories.
Some designers are even incorporating interactive elements into their garments, such as LED lights, sensors, and other electronic components, which can be controlled by smartphones or other devices. This creates a new level of interactivity and engagement between the wearer and the garment, and opens up new opportunities for creative expression and innovation in fashion design.
Digital Art for Music and Performance Art
Digital art can be used in music and performance art in a number of ways. For example, musicians can use digital art in their music videos or album artwork to create visual representations of their music. They can also use digital technology to create live visuals during their concerts or shows, enhancing the overall sensory experience for their audience.
In performance art, digital art can be used to create interactive installations or immersive experiences for the audience. For example, a performance artist might use projection mapping or augmented reality to create a live, interactive performance that blurs the line between the physical and digital worlds. Digital art can also be used to create unique, custom-designed costumes and set pieces that are tailored specifically to a particular performance or show.
Digital Fine Art
Digital art has disrupted the traditional fine art world, transforming the way we create, view, and sell art. The advent of digital tools and software has opened up new creative avenues for artists, allowing them to experiment with different techniques, styles, and mediums that were not previously available. This has led to the emergence of new forms of digital art, such as generative art, algorithmic art, and interactive art, which challenge traditional notions of what art is and can be.
Digital art has also made it easier for artists to explore social, cultural, and political issues in their work, creating thought-provoking pieces that comment on the world around us. For example, some digital artists use virtual reality technology to immerse viewers in an interactive environment that raises awareness of a particular issue.
In addition to its artistic value, digital art has also gained significant commercial value, with digital works selling for millions of dollars at auction houses and online marketplaces. This has led to a new wave of digital art collectors and investors, who recognise the potential of digital art as a valuable asset. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more innovative and exciting uses of digital art in the fine art world.
What Does the Future Hold for Digital Art?
The future of digital art is expected to be shaped by a number of technological advancements and innovations. For example, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to lead to new forms of generative art, where algorithms and machines can create art on their own without human intervention. This could lead to a new era of creativity and experimentation, where artists can push the boundaries of what is possible with digital art.
Virtual and augmented reality are also expected to play a big role in the future of digital art. These technologies allow artists to create immersive, interactive experiences that can be experienced by viewers in new and exciting ways. In addition, blockchain technology is being used to create digital art that is scarce and unique, allowing artists to create and sell one-of-a-kind works of art.
In the coming years, digital art is expected to continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with technology and art, opening up new opportunities for artists, collectors, and art enthusiasts alike. As digital tools and techniques become more sophisticated and accessible, we can expect to see a new wave of creativity and innovation in the world of art.
Final Thoughts
Digital art is a rapidly evolving field that has opened up new possibilities for artists to create innovative and engaging works of art. With new technologies such as AI, VR, and AR, the possibilities for digital art are endless. The digital art market is also expanding rapidly, with new platforms and marketplaces emerging to connect artists with collectors and buyers.
As the field continues to grow and evolve, it will be interesting to see how artists continue to push the boundaries of what is possible and create new and exciting works of digital art.
