Business Transformation Methodology
BTM² was the world's first holistic business transformation management methodology that provides a framework with clear phases, deliverables and corresponding methods. It was developed by Professor Dr. Axel Uhl, University of Applied Sciences Luzern, Switzerland and published in the book Uhl, A. and Gollenia, L. A. (eds.), A Handbook of Business Transformation Management Methodology.
To learn more about BTM² and a new course and certificate go to btm2method.com
Business Transformation Methodology Podcast Episode
Business Transformation Methodology Transcript
Companies the world over are embarking on all sorts of digital business transformation journeys, and while they adopt a variety of well-known best practices such as PMP or PRINCE2 for project management, MSP Programme Management, ITIL for IT services, Scrum for building products, or the agile manifesto, etc. – how many have adopted a best practice Business Transformation Management approach?
The truth is, not many. And studies by impartial academic and research organisations reinforce that statement. It's one reason why so many companies are struggling either to orchestrate transformation, or to indulge themselves in anything more than digital sugar coating.
The Business Transformation Management Methodology – or BTM² for short – is a four-phase holistic and integrated business transformation management methodology. It was developed by a think-tank (once known as The Business Transformation Academy) based in Switzerland, consisting of senior transformation practitioners, leaders from well-known global brands and leading academics, and led by Professor Dr. Axel Uhl.
BTM² is an intensely documented approach to holistic business transformation management, which addresses the transformation journey from the start.
It's often said that strategy is three times more difficult to deploy than develop, which explains why so many strategies result in a painful execution journey for everyone involved. Budgets and timelines expand, and stakeholders get tired of the noise that comes from a poorly orchestrated transformation.
The benefits on display in the business case begin to fade away as it becomes clear that the planned return on investment is diminishing as more time and resources are pumped into the initiative. This is not to mention the fact that the people and business units aren't prepared for what lies ahead.
This is a reality in many companies, because they lack the right transformation tools and capabilities. The BBC's failed £100 million Digital Transformation is one example, and thousands of others are swept under the carpets of companies that thrive on operational excellence, but discover to their cost that, transformation excellence requires a very different set of capabilities.
BTM² was the world's first holistic business transformation management methodology that provides a framework with clear phases, deliverables and corresponding methods. It's a generic framework that can be applied to different business transformation use cases, and it isn't specific to one business function, technology or industry.
In its most simple form, there are four phases in the of BTM² transformation lifecycle, which are; Envision, Engage, Transform, and Optimise. This is the continuous lifecycle of business transformation. While projects start and end, business transformation needs to be a continuous cycle.
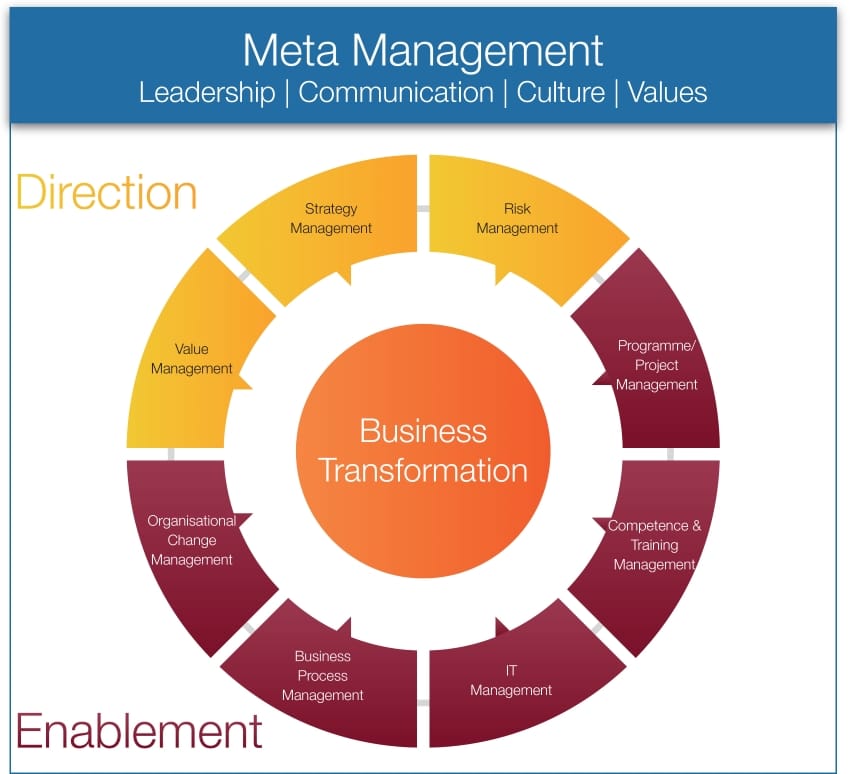
BTM² consists of nine transformation management disciplines. Let me quickly list them, and then take a closer, albeit very high-level look at each.
Meta Management
Meta Management is about Leadership, Culture, Values, Communication.
Then we have Transformation Direction, which consists of Strategy Management, Value Management, and Risk Management.
Next there's Transformation Enablement, which is made up of five individual management disciplines. These are, Project and Programme Management, Business Process Management, IT Transformation Management, Organisational Change Management, and Competence and Training Management.
Now let's explore each of the nine management disciplines, starting with Meta Management.
In the context of business transformation, Meta Management provides the overarching frame for a business transformation. It also provides the linkages among the disciplines and also the management structure, which allows the transformation process to be effective. It addresses individual disciplines which include guidelines, leadership, culture, values, and communication.
Strategy Management
Next is Strategy Management which primarily addresses the Envision phase of the transformation life-cycle, during which a strategy is developed. Strategy Development involves the selection of appropriate team members, collection of data, analysis of transformation needs and readiness. It also involves the design of a business vision, a business model and the definition of an integrated transformation plan.
Value Management
Next is Value Management, which involves defining the business benefits and the changes needed to realise them. It also includes evaluating the feasibility of making the changes successfully and producing an evidence-based business case and supporting benefits realisation plan. Value Management relies heavily upon the engagement of stakeholders in the preparation of the business case and benefits plan to create the knowledge and commitment required to realise the benefits described in the business case.
Risk Management
Risk management provides fundamental guidance to the planning, development and effective execution of a business transformation. It's vital that the risks related to the process of transforming an organisation towards a desired future state are well-managed. Along with risks that relate more to the possibility that this desired state quickly becomes either obsolete or inadequate.
Programme and Project Management
Then we have Programme and Project Management, which aims to support the implementation of the transformation strategy in order to achieve the benefits described in the business case. Programme management focuses on high-level specification and the “why and what” of transformation. It includes stakeholder management, benefit realisation, dependency management, transition management/change acceptance and integration with corporate strategies. While Project management focuses on detailed specification and the “how” of implementation, along with control of activities to produce products.
Business Process Management
Next, we have Business Process Management, which defines the scope of process changes needed for the expected improvements in performance. To make the transformation effort a continuous success, business processes have to be considered from a strategic perspective. The identification of end-to-end business processes and the assignment of responsible process owners is a major task. It's important to understand that process management doesn't equal process modelling, but rather the relationship between IT, Business and People.
IT Transformation Management
Then there's IT Transformation Management, which evaluates the impact of current IT processes, competencies and systems on business transformation, and vice versa. It assesses and enables solution readiness of the business, defines and assesses the gap between the as-is and to-be of IT, deploys IT operations and services, and implements IT governance. It also involves improving IT operations and services and managing the IT lifecycle.
Organisational Change Management
Organisational Change Management – or OCM as it's commonly known – addresses the human element of business transformation. It deals with the people who have to change their ways of working and involves setting up a foundation for effective OCM with respect to governance and assessing organisational change readiness. Establishing and implementing stakeholder communication and performance management strategies, and continuously receiving feedback to make improvements is key.
Competence and Training Management
The ninth transformation management discipline is Competence and Training Management, which provides qualification and enablement with respect to the competences required for business transformation, and the strategic core competences vital for the company's future success. Competence and Training Management identifies and analyses training needs and objectives, develops training measures and implements the learning process.
If digital business transformation efforts are to be successful, all of the above nine transformation management disciplines need to be adequately addressed, and it's worth noting that technology is just one of the nine disciplines in the list. This really highlights the fact that transformation is less about technology and more about people and business.
Organisations need to ensure that their digital business transformation leaders avoid the pitfall of placing an unbalanced emphasis on technology, process and some project management, while paying lip-service or light touches to the other transformation management disciplines. Research has shown that this common error is the basis for countless failed and struggling transformation programmes throughout the world.
BTM² is an integrated and holistic business transformation management methodology that can help firms avoid the pitfalls that over 70% fall into.
As in any profession, theory is necessary, but the capability to bring those theoretical best practices and good intentions to life is what separates the best transformation leaders from the rest.
BTM² helps great managers and leaders complement their existing core capabilities with the new transformation capabilities they need to step up into the complex world of digital business transformation. While a leader might have one or two decades of operations under their belt, orchestrating transformation is a brand-new challenge for many of them. But they can complement their previous experience with a new way of thinking and working.
The ability to orchestrate the entire business transformation is essential if the performance is to be one that people want to hear. Without it, the tune will be one of noise that no stakeholder expects to pay for. On the other hand, with the right leadership, the transformation could become one of the company's finest performances that its people are proud to be part of.
Why use BTM²?
Well, BTM² is based on extensive academic research and commercial experience. It helps its adopters build credibility among their business peers, and it's an objective, unbiased framework to identify and solve business challenges.
BTM² is an ideal tool for regular and quick assessments of business transformation, and it addresses both the rational and irrational aspects of transformation.
The methodology distinguishes managers and leaders who use a proven approach to transformation, from those that can't articulate an approach that everyone understands.
BTM² isn't focused on any particular technology or company, and it's open for any organisation to use without having to engage the consulting or integration firms that will seize every opportunity to land and expand.
To learn more about BTM² go to btm2method.com
I appreciate you listening, and here's a quote to finish off the day from Brian Lawley.
Methodology must be flexible. Companies often don't adopt the materials and methods they were trained on because they aren't flexible enough.
What flexible methodology is helping your company undertake a meaningful transformation?
I hope you enjoyed this episode. Thanks for listening – Take care and I'll catch you in the next episode of transformation management. Bye.
