What is Business Transformation?
Business transformation refers to the process of fundamentally changing the way an organisation operates in order to achieve its strategic goals. This can involve a wide range of changes, such as adopting new business models, implementing new technologies, restructuring processes and operations, and redefining the organisation's overall strategy.
The goal of business transformation is to improve the organisation's performance and competitive advantage in the marketplace. This often requires a significant cultural shift within the organisation, as well as a willingness to embrace new ways of thinking and working. Successful business transformation can result in increased efficiency, better customer experience, and long-term growth for the organisation.
The Evolution of What is Business Transformation
Business transformation has been an important concept in management and strategy for several decades, evolving over time as businesses face new challenges and opportunities. In the past, business transformation primarily focused on process improvements and cost cutting measures to streamline operations and boost efficiency. However, as the business landscape has become increasingly complex and digital, the scope of business transformation has expanded to include broader strategic initiatives such as digital transformation, innovation, and customer-centricity. Today, business transformation is seen as a critical tool for organisations to adapt to change, stay competitive, and create value for stakeholders.

What are the Drivers of Business Transformation?
There are several drivers of business transformation, including:
Technology advancements
Technology is constantly evolving, and companies need to keep up with these advancements to remain competitive.
Customer demands
Changing customer expectations and preferences require companies to adapt their products, services, and processes to stay relevant.
Market forces
Globalisation, increased competition, and changing industry dynamics can drive companies to transform their business to remain competitive.
Regulatory requirements
Changes in laws and regulations can force companies to transform their business processes and operations.
Organisational culture
Companies that want to improve their performance, productivity, and innovation often need to transform their organisational culture.
Mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions can trigger business transformation initiatives as companies integrate their operations and processes.
Cost reduction
Companies may undertake business transformation initiatives to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Strategic goals
Companies may undertake business transformation initiatives to achieve strategic goals, such as expanding into new markets, launching new products, or diversifying their business.
These drivers can be interrelated and may require a coordinated effort to address effectively.
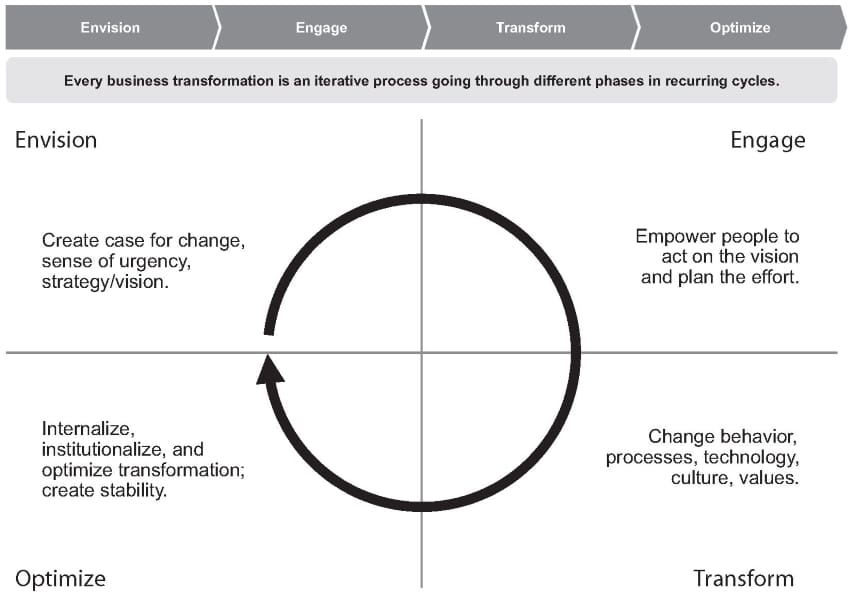
4 Phases of Business Transformation
There are four phases in the BTM² business transformation methodology lifecycle, which are:
Envision: Create a case for change, a sense of urgency, strategy, and vision.
Engage: Empower people to act on the vision and plan the business transformation.
Transform: Change processes, technology, behaviour, culture, and values.
Optimise: Internalise, institutionalise, and optimise transformation. And create stability.
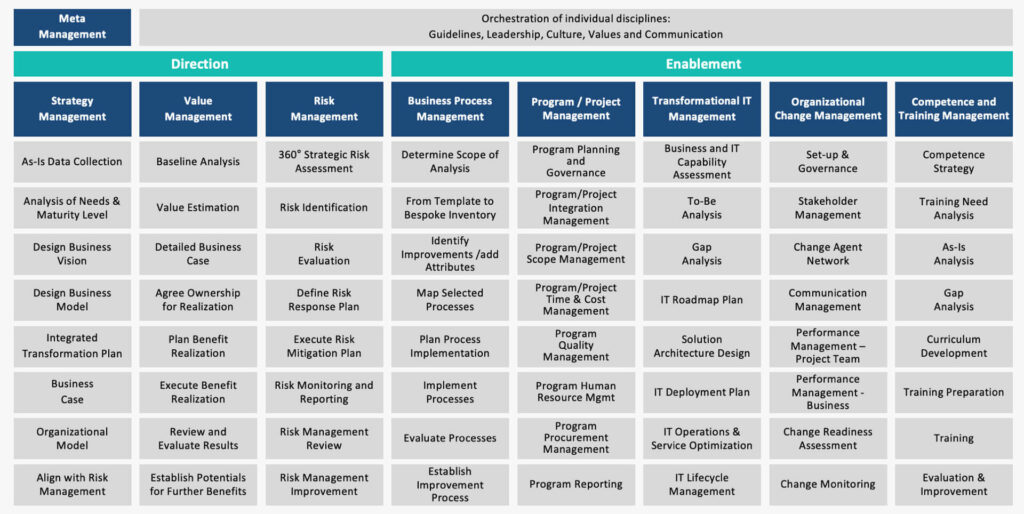
9 Management Disciplines of Business Transformation
The BTM² business transformation methodology consists of nine transformation management disciplines which are:
Meta Management (Leadership, Culture, Values, Communication)
Strategy Management (Transformation Direction)
Value Management (Transformation Direction)
Risk Management (Transformation Direction)
Project and Programme Management (Transformation Enablement)
Business Process Management (Transformation Enablement)
IT Transformation Management (Transformation Enablement)
Organisational Change Management (Transformation Enablement)
Competence and Training Management (Transformation Enablement)
Learn more about these business transformation management disciplines.
4 Main Types of Business Transformation
Radical Business Transformation
Radical transformation is a significant change to a company's strategy and approach, resulting in the creation of a new business model and vision. It often requires an overhaul of the organisation's core values and principles, as well as a significant shift in culture and mindset.
This type of transformation is often driven by external market factors or the need to pivot in response to changing industry trends. It requires a strong commitment from leadership and a willingness to take bold risks to ensure long-term success.
Architectural Business Transformation
Architectural transformation refers to the process of restructuring an organisation's technology infrastructure and systems while maintaining its core business processes. This involves a significant change in the underlying technology and infrastructure of the organisation but does not necessarily change the overall strategic goals or direction of the business.
By focusing on optimising and modernising its technology architecture, an organisation can better support its operations and improve efficiency. This often involves updating legacy systems, implementing new software, and integrating new technologies to support business operations. A successful architectural transformation can help organisations stay competitive in today's rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Modular Business Transformation
Modular transformation refers to a scenario in which the organisation modifies some core elements of its design while keeping the overall enterprise architecture intact. This approach allows companies to implement targeted changes that address specific challenges without disrupting the entire system. For example, a company may choose to update its production line or supply chain processes while keeping its organisational structure and IT infrastructure intact.
By using this strategy, organisations can achieve incremental improvements while minimising the risk and cost associated with a full-scale transformation. This approach can help organisations remain agile and adapt to changing market conditions more efficiently.
Incremental Business Transformation
Incremental transformation involves making small, continuous improvements to the enterprise design with minimal changes to technology and operations. This approach allows the organisation to refine and extend its existing processes and capabilities, while minimising disruptions to daily operations. Incremental transformation often involves a gradual and continuous improvement process that allows the organisation to stay competitive
by adapting to changing market conditions and customer needs. It requires a focus on continuous improvement and a willingness to adopt new technologies and processes as needed to drive long-term success.
What is Impacted During Business Transformation?
There are several aspects of an organisation that are impacted by business transformation, including:
Strategy
Involves a change in the company's strategy, vision, and direction to respond to new market trends or opportunities.
Operations
Focuses on improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and optimising business processes to improve performance and profitability.
Culture
Involves changing the organisation's culture, values, and behaviours to foster innovation, collaboration, and customer-centricity.
Structure
Involves changing the organisation's structure, such as reorganising teams, creating new roles, or consolidating business units, to improve agility and decision-making.
Technology
Involves leveraging digital technologies to fundamentally change the way a company operates, interacts with customers, and delivers value to the market.
Other aspects of an organisation are impacted by business transformation. The key is to identify and manage these impacts in a way that does not compromise the achievement of the transformation goals.
What is The Difference Between Business Transformation and Digital Transformation?
While business transformation and digital transformation are related concepts, they have different scopes and objectives.
Business transformation refers to the process of fundamentally changing the way an organisation operates to achieve its strategic goals, which may or may not involve technology. Business transformation may include a wide range of changes such as organisational restructuring, changes to business processes, new business models, and strategic realignment.
Digital transformation, on the other hand, specifically refers to the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, resulting in fundamental changes to how the business operates and delivers value to customers. The goal of digital transformation is to create a more agile, responsive, and data-driven organisation that can compete in a rapidly changing digital environment. This may involve adopting new technologies, leveraging data and analytics, and creating new digital products and services.
In summary, while both business transformation and digital transformation involve significant changes to an organisation, the former is broader and may involve non-digital changes, while the latter specifically focuses on the integration of digital technology to drive business success.
What Should a Chairman Know About Business Transformation?
As a key member of a company's leadership team, a Chairman plays a critical role in the success of any business transformation effort. Here are some key things that a Chairman should know about business transformation:
The importance of having a clear vision and strategy: Business transformation requires a clear vision of where the company is going and a well-defined strategy for getting there. The Chairman must ensure that the vision and strategy are aligned with the company's goals and objectives.
The need for effective change management: Business transformation often involves significant changes to the company's processes, systems, and culture. The Chairman must ensure that change is managed effectively, with clear communication to all stakeholders, and a plan for addressing any resistance to change.
The importance of collaboration: Business transformation is a team effort, requiring collaboration across departments and functions. The Chairman must ensure that there is a culture of collaboration and that the necessary resources are made available to support the effort.
The role of technology: Business transformation often involves the use of new technologies to improve business processes and drive innovation. The Chairman must ensure that the company has the necessary technology infrastructure and expertise to support the transformation effort.
The need for ongoing evaluation and adjustment: Business transformation is an ongoing process that requires ongoing evaluation and adjustment. The Chairman must ensure that there are metrics in place to measure progress, and that the company is willing to adjust as needed to stay on track.
In summary, a Chairman plays a critical role in ensuring the success of any business transformation effort. By focusing on clear vision and strategy, effective change management, collaboration, technology, and ongoing evaluation and adjustment, the Chairman can help lead the company through a successful transformation.
What Should a CEO Know About Business Transformation?
CEOs play a critical role in driving successful business transformations. Here are some key things that CEOs need to keep in mind:
Vision: The CEO must have a clear and compelling vision for the transformation that is aligned with the company's overall strategy and goals.
Culture: The CEO needs to drive a culture of innovation and agility that supports the transformation. This may involve shifting the organisation's mindset and embracing new ways of working.
Communication: The CEO must communicate the transformation strategy clearly and frequently to all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors.
Talent: The CEO needs to ensure that the organisation has the right talent and capabilities to execute the transformation. This may involve hiring new talent or upskilling existing employees.
Metrics: The CEO must establish clear metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the transformation and ensure that progress is being made.
Governance: The CEO must establish a governance framework to manage the transformation and ensure that it stays on track.
Collaboration: The CEO needs to collaborate with other leaders and stakeholders to ensure that the transformation is aligned with their goals and priorities.
By keeping these factors in mind, CEOs can successfully lead their organisations through a business transformation, achieve their strategic objectives, and drive long-term success.
What Should Other Key Executives Know About Business Transformation?
Business transformation is not just limited to CEOs, but other C-level executives also need to be aware of it as it can affect various aspects of the business. Here are some things that other C-level executives should know about business transformation:
Understanding the goals: All executives should have a clear understanding of the goals and objectives of the business transformation. This will help them to align their departments and work towards achieving the transformation goals.
Collaboration: Business transformation involves cross-functional collaboration and coordination, which means executives need to work together and leverage each other's expertise to achieve the desired outcomes.
Change management: Business transformation requires significant changes in the organisation, which can be difficult for employees. C-level executives should be aware of the change management process and ensure that employees are adequately supported during the transition.
Innovation: Business transformation is often driven by innovation, and C-level executives should be open to new ideas and technologies that can enable the transformation.
Customer-centricity: Business transformation is not just about internal changes but also about meeting the changing needs of customers. C-level executives should prioritise customer-centricity in their decision-making to drive successful transformation.
Who Should Lead Business Transformation on a Day to Day Basis?
The person who leads business transformation on a day-to-day basis is typically a program or project manager, who is responsible for managing the various initiatives and activities involved in the transformation process. The program or project manager is usually a seasoned professional with expertise in project and change management, as well as experience in the specific areas of the business being transformed. This individual works closely with executive leadership, stakeholders, and other key personnel to ensure that the transformation process is on track and aligned with the organisation's overall strategic goals. They are also responsible for monitoring progress, identifying, and mitigating risks, and adjusting the transformation plan as needed.
How do You Manage Business Transformation?
Managing business transformation involves leading the implementation process, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and working towards the same objectives, and making necessary adjustments as the transformation progresses. The following are some key steps to effectively manage business transformation:
Develop a clear vision and strategy: A clear and concise vision for the transformation and a well-defined strategy for achieving that vision is essential. It should be communicated to all stakeholders to ensure everyone is aligned.
Establish a governance structure: A governance structure is important to provide oversight and decision-making authority during the transformation. This should include a steering committee, a project management office (PMO), and other necessary teams.
Define key performance indicators (KPIs): KPIs should be defined to measure the success of the transformation. These should be regularly tracked and communicated to stakeholders.
Engage and empower employees: Employees should be engaged in the transformation process from the beginning. They should be empowered to take ownership of the changes and help drive the transformation forward.
Manage risks: It is important to identify potential risks to the transformation and develop mitigation plans. These plans should be regularly reviewed and updated as needed.
Monitor progress: The transformation process should be regularly monitored to ensure that it is progressing according to plan. Adjustments should be made as necessary to keep the transformation on track.
Celebrate successes: Celebrating successes along the way can help maintain momentum and keep stakeholders motivated and engaged.
By effectively managing business transformation, organisations can successfully navigate change and achieve their goals for growth and innovation.
What is The Business Transformation Management Methodology?
The Business Transformation Management Methodology (BTM²) is a comprehensive framework for managing and delivering large-scale business transformations. It was developed by a think tank of xxx and funded by the SAP company.
BTM² is widely used in by many of the world's best business transformation managers, leaders, and consultants.
The methodology is based on a four-phase approach that includes four phases and nine management disciplines.
Each phase includes a set of activities and deliverables, such as assessing the current state of the business, defining the target state, developing a roadmap, executing the transformation plan, and monitoring and measuring the results. The BTM² methodology emphasises the importance of involving stakeholders, managing change, and ensuring the alignment of business and IT objectives.
Best Practices for Successful Business Transformation
In addition to adopting a business transformation management framework such as BTM² here are some general best practices for a successful business transformation:
Develop a clear vision
Start with a clear and well-defined vision of what you want to achieve through the transformation. This will help you stay focused and aligned throughout the process.
Involve stakeholders
Engage and involve all relevant stakeholders in the transformation process, including employees, customers, partners, and suppliers. This will help you get buy-in and support, as well as gather valuable input and feedback.
Develop a comprehensive plan
Create a detailed plan that outlines the goals, timelines, resources, and activities required for the transformation. This plan should also identify potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Prioritise and sequence initiatives
Prioritise and sequence initiatives based on their potential impact and feasibility. This will help you focus on high-impact initiatives that can deliver quick wins, while also ensuring a smooth and phased transition.
Invest in change management
Develop a robust change management program that focuses on communication, training, and employee engagement. This will help you manage resistance, build awareness, and create a culture that is open to change.
Leverage data and analytics
Use data and analytics to gain insights into the performance of your organisation and identify areas that require improvement. This will help you make data-driven decisions and measure the impact of your transformation initiatives.
Embrace innovation
Foster a culture of innovation and experimentation and encourage employees to come up with new ideas and approaches. This will help you stay ahead of the curve and continuously improve your business.
Monitor and measure progress
Monitor and measure the progress of your transformation initiatives, and adjust your plans and strategies as needed. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you are achieving your goals.
Overall, successful business transformation requires a strategic and holistic approach that engages stakeholders, prioritises initiatives, invests in change management, leverages data and analytics, fosters innovation, and continuously monitors and measures progress.
5 Business Transformation Case Studies
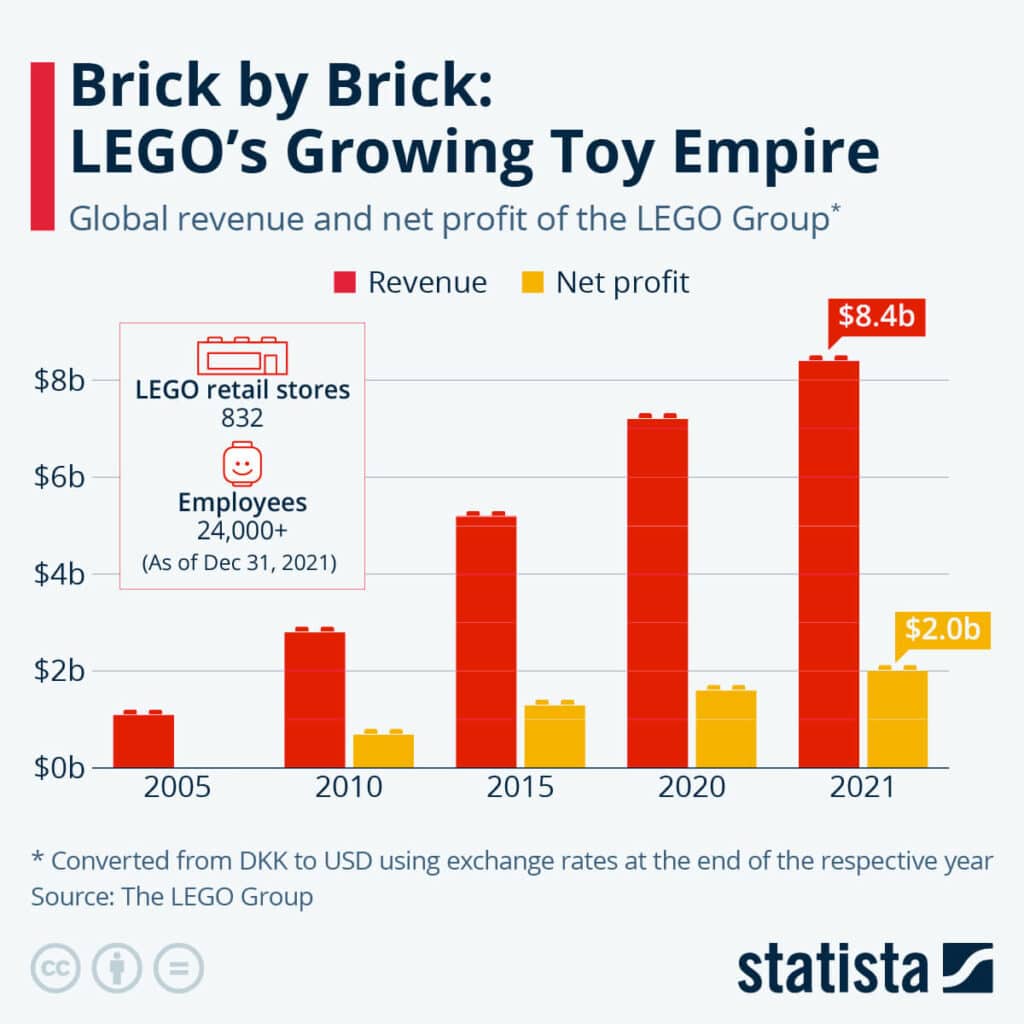
Lego Business Transformation
In the early 2000s, the Danish toy manufacturer was facing serious financial difficulties due to declining sales and changing consumer preferences. The company was on the verge of bankruptcy, but instead of giving up, Lego embarked on a major business transformation initiative. The company restructured its operations, divested non-core businesses, streamlined its supply chain, and refocused its product lines.
One key element of the transformation was the introduction of the Lego Movie, which helped reinvigorate the brand and drive sales. Today, Lego is a thriving company with a strong global brand and a diverse range of product lines. The success of Lego's business transformation is a testament to the power of strategic planning, innovation, and a willingness to embrace change.
Ford Business Transformation
In recent years, the Ford motor company has been facing challenges from new players in the automotive industry, as well as rising customer demands for new features and technologies.
Business Transformation Initiative: In 2018, Ford announced a major business transformation initiative aimed at modernising its operations and transitioning to become a mobility company. The initiative involved several key components, including:
Reorganising the company's global business operations to streamline decision-making and improve efficiency.
Investing heavily in electric and autonomous vehicle technology, with plans to introduce a range of new EV models in the coming years.
Partnering with tech companies to develop new mobility solutions, such as ride-sharing services and delivery fleets.
Focusing on improving customer experience, with a renewed emphasis on digital channels and personalised services.
While the full impact of Ford's business transformation initiative has yet to be realised, the company has already made significant progress in several key areas. For example, Ford has launched several new electric and hybrid models, including the Mustang Mach-E and the F-150 Lightning, which have been well-received by customers and critics alike. The company has also partnered with tech companies like Argo AI and Rivian to accelerate the development of autonomous vehicle technology.
Ford also invested in a range of new mobility solutions, such as its GoRide health transportation service and the delivery-focused Ford Pro division. Overall, Ford's business transformation initiative has positioned the company to better compete in a rapidly evolving automotive industry and to meet the changing needs of its customers.
General Electric
General Electric (GE) is a massive conglomerate with diverse business units spanning multiple industries. In recent years, the company has undergone a significant business transformation to streamline its operations and refocus on its core strengths. The transformation involved divesting non-core businesses and reducing the size of the organisation, among other initiatives. As a result of these efforts, GE has become a leaner, more efficient company with improved profitability. The business transformation has allowed GE to focus on its core strengths and position the company for long-term success.
Pepsico
In 2019, PepsiCo announced a new business transformation initiative to become a more consumer-centric, faster, and more agile organisation. The main goals of the business transformation initiative were to increase productivity, accelerate growth, and create a more sustainable business model. To achieve this, PepsiCo aimed to streamline its operations, enhance its digital capabilities, and invest in new product development and marketing.
To drive the business transformation, PepsiCo implemented a range of initiatives, including:
- Investing in automation and digitalisation to streamline operations and increase efficiency.
- Enhancing its e-commerce capabilities and online presence to better engage with consumers and improve customer experience.
- Expanding its product portfolio to include more healthy and sustainable products, in response to changing consumer preferences.
- Improving its supply chain and logistics operations to increase speed and flexibility.
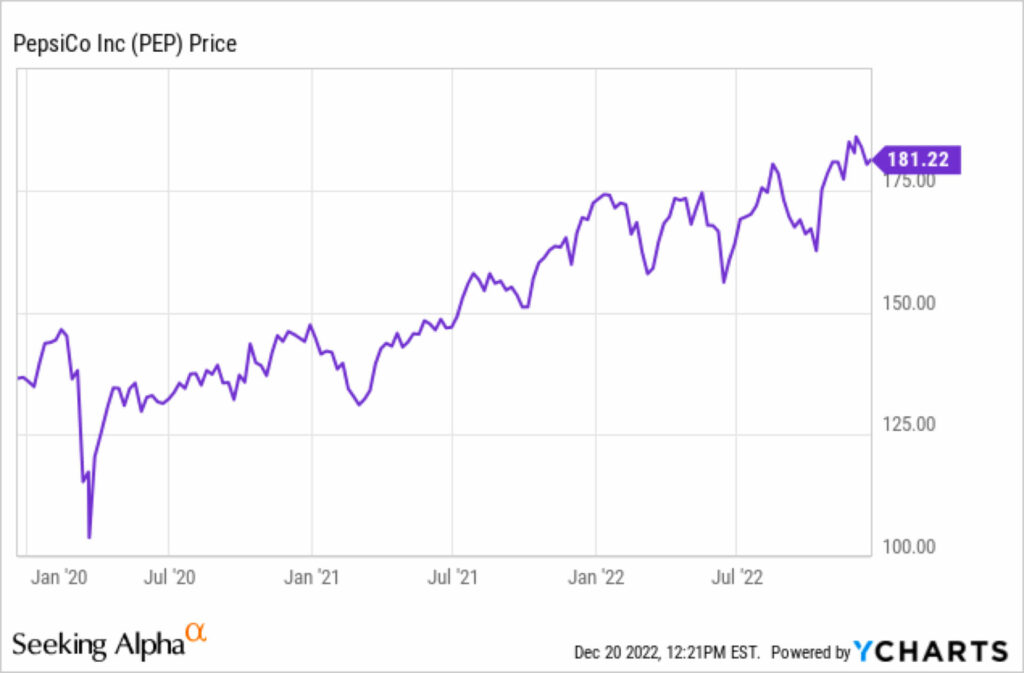
As a result of the business transformation, PepsiCo was able to increase productivity and reduce costs, while also expanding its market share and improving its sustainability credentials. For example, in 2020, the company reported an increase in revenue and net income, driven by strong performance in its snacks and beverage businesses, as well as its focus on innovation and sustainability. PepsiCo was also recognised as one of the most ethical companies in the world by the Ethisphere Institute in 2021, reflecting its commitment to social responsibility and sustainability.
BBVA
The global financial group BBVA has undergone a significant business transformation in recent years. The transformation was initiated with the goal of becoming a more customer-centric, agile, and innovative organisation. To achieve this transformation, BBVA adopted a new organisational model, which included the creation of cross-functional teams, the implementation of agile methodologies, and the adoption of new technologies such as cloud computing, big data, and artificial intelligence. BBVA also introduced new digital products and services, such as a mobile banking app and a digital wallet, to improve the customer experience.
The transformation has resulted in significant improvements for BBVA. The bank has seen an increase in customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as improved employee engagement. The bank has also been recognised for its innovative approach, winning awards for its mobile banking app and other digital initiatives.
BBVA's business transformation demonstrates the importance of embracing new technologies, adopting an agile mindset, and putting the customer at the center of the organisation.
Do We Need a Consulting Firm to Help With Business Transformation?
The decision to hire a big consulting firm or an independent consultant for business transformation ultimately depends on your organisation's specific needs, budget, and resources.
Big consulting firms often have a wealth of resources and expertise, with large teams that can tackle complex projects and a wide range of experience across various industries. However, their services can come at a premium cost and may not be feasible for smaller organisations.
Independent consultants, on the other hand, typically offer a more personalised and customised approach, with more affordable rates and the ability to provide more direct access to senior-level expertise. They may also have a more flexible approach to project management and can often be more adaptable to changes and unexpected challenges.
Business transformation consultants employed by big firms will typically put their own firm's interests ahead of yours, whereas an independent consultant isn't burdened by a boss, which means they can always act in your best interests rather than those of their employer.
Ultimately, the choice of whether to hire a big consulting firm or an independent consultant should be based on a careful evaluation of your organisation's needs, resources, and budget, as well as a review of the consultant's relevant experience and track record of success.
Business Transformation Management Course
If you want to equip yourself with the expertise required to orchestrate business transformation the BTM² Business Transformation Management course will help you.

